
PVC-U windows mean sustainability
Sustainability is an essential aspect in building. This requirement can be met very well with modern vinyl windows - and not only because of their good thermal insulation and the associated energy savings. Even the production of window profiles today can be carried out with comparatively low energy and resource consumption. The practically complete recyclability of old windows has a particularly favourable effect.

Table of contents
- Sustainability: An old concept
- The entire life cycle in view
- Sustainability begins with profile production
- Keep valuable energy in the building
- Recycling provides new raw material
Sustainability: An old concept
With the growing awareness of environmental and climate protection, the desire for sustainable construction is growing. This applies above all to private construction and modernization projects, but also in the commercial and institutional sectors. In fact, resource- and energy-saving buildings can do much to noticeably reduce emissions of climate-damaging greenhouse gases: According to estimates, more than a third of emissions worldwide come from the building sector. If we consider only Germany, the share is still around one-seventh.
Regeneration sets the framework
The idea of a sustainable economy and way of life is not new. The concept was first formulated in concrete terms more than 200 years ago - in connection with the management of forests, which were to provide stable timber yields in the long term. Sustainability here means that trees are not felled faster than new ones can grow. Transferred to other areas, this means that all resources and the environment are only stressed as much as their regeneration allows.

The entire life cycle in view
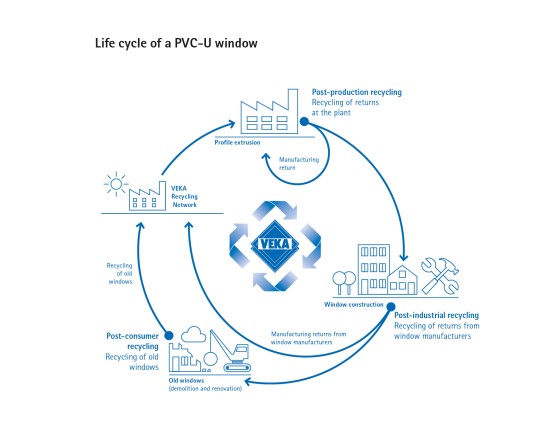
A comprehensive approach is required to assess whether or not a building is sustainable overall. In principle, therefore, all building materials and building elements must be considered, from their manufacture through their use to the end of their life cycle. Added to this are the energy and resources required for construction and ultimately also for demolition. Even for a small, simple building, such a detailed analysis would require enormous effort. It is greatly simplified by the fact that individual balances are already available for most components, for example for the window.
Sustainability begins with profile production
The window is a good illustration of the factors that influence the sustainability balance. This is particularly true for plastic windows. New production of the material PVC for the window profiles uses petroleum - a non-renewable raw material. However, since the recycling of plastic windows produces high-quality PVC recyclate that can be used directly again in profile production, the situation here has improved greatly. At VEKA, for example, more than a quarter of the PVC used for extrusion already comes from recycling.
In profile extrusion, there are further starting points for more sustainability. Here, a lot can be achieved with comparatively simple measures, for example at VEKA's headquarters: The process water used to cool the extruders and calibers is taken from the specially created wetland biotope. It is then available again for process cooling. Every year, around 136 million litres of water circulate through this system - an amount of water that does not have to be taken from the public networks.
In terms of electricity consumption, VEKA's profile production also demonstrates the enormous steps that can be taken to conserve resources. Not least thanks to suggestions from the company's own workforce, it has been possible to optimize many aspects - both in Sendenhorst and at the Group's other sites. In addition, the company relies on solar power from the large hall roofs. The reward for this commitment is that electricity consumption has been halved since 2005.

Keep valuable energy in the building
In addition to the manufacture of the window profiles, the insulating effect of the windows is an important aspect of sustainability. This becomes particularly clear when comparing the energy losses of outdated and modern buildings: In the former case, about half of the heat losses are due to the windows, in the latter it is only about one tenth. Replacing old windows with modern windows with their more effective thermal insulation alone is therefore a worthwhile modernization measure that has a noticeable effect on heating requirements.
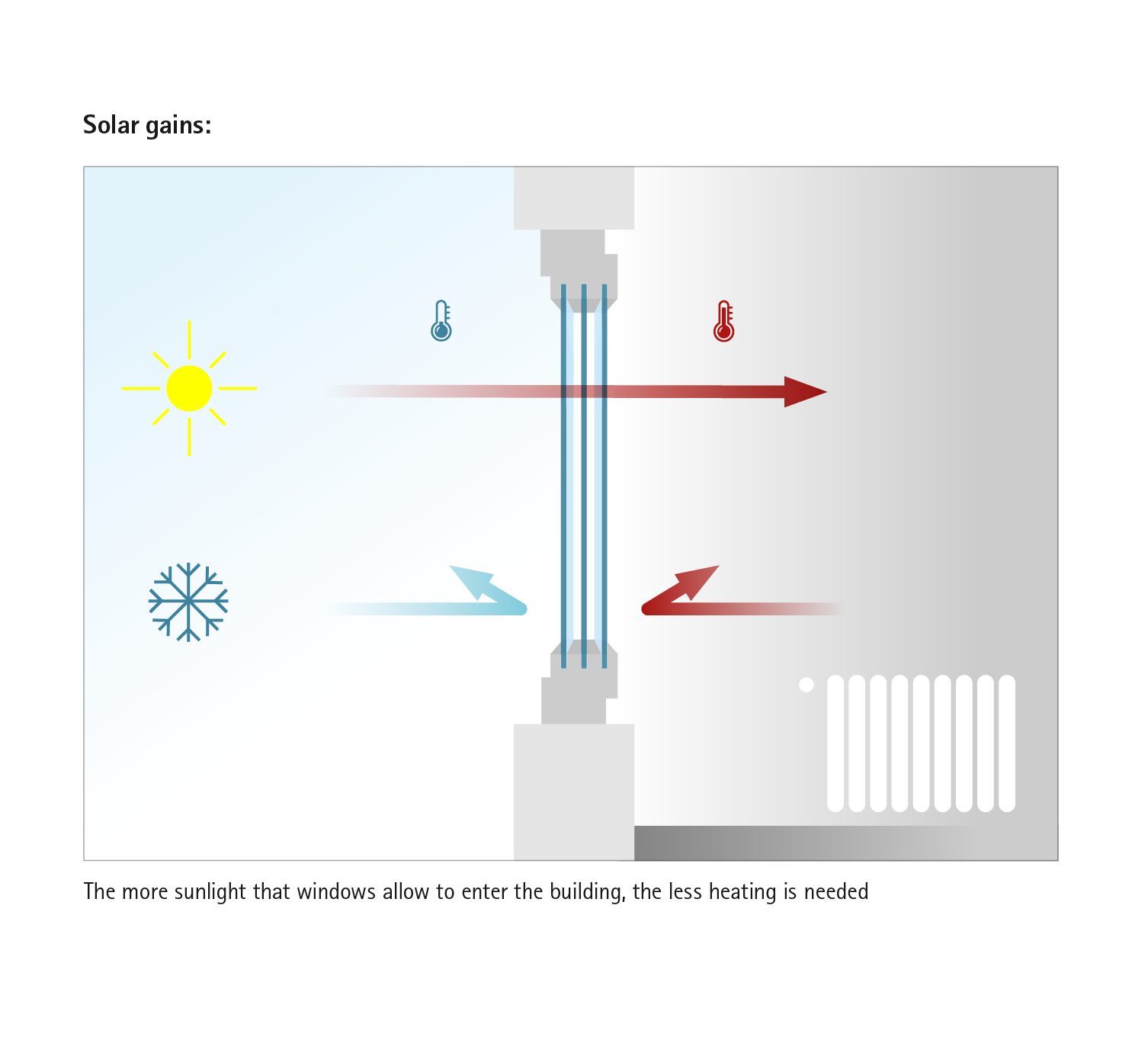
Added to this are the solar gains - here, the trend towards ever larger elements has a further reinforcing effect. In addition to more daylight, modern, large-area windows and doors also mean more thermal energy, which they retain very effectively in the building. When outside temperatures are cool or cold, they achieve a significant reduction in heating requirements in this way. Excessive heating in summer can be easily prevented with modern shading solutions.
Recycling provides new raw material
With modern windows, builders and architects can take a big step towards sustainable construction. Finally, an important contribution is made by problem-free recycling - regardless of the frame material, because profiles made of PVC-U and aluminium can be recycled just as easily today as those made of wood. This is an essential factor for the overall ecological balance of a window.
As a recycling pioneer, VEKA demonstrated back in the early 1990s how old PVC-U windows could be recycled on an industrial scale, both effectively and economically. Since then, the VEKA recycling group has continued to expand its activities: In addition to the pilot plant in Behringen, Thuringia, it now operates two other plants in France and the UK. Here, a total of around 100,000 tonnes of windows and doors, roller shutters and also PVC production waste can be recycled per year.
The multi-stage recycling process delivers unmixed PVC granules that can be immediately reused for the extrusion of new PVC-U profiles, plastic pipes and other products. In addition to the recyclate, there are also metal, glass and rubber fractions that can be recycled. PVC-U windows and doors are thus almost completely recyclable. Material cycles are closed, energy requirements are minimized and disposal is virtually unnecessary.